The dogma that neurogenesis slows to a trickle in the aging human brain has been significantly challenged this week. A groundbreaking study published in Nature (February 25, 2026), led by scientists at the University of Illinois Chicago and the Northwestern University SuperAger Program, reveals that SuperAgers produce neuroblasts at rates far higher than their age-matched peers.
SuperAgers are defined as adults over age 80 whose episodic memory performance matches or exceeds that of people 30 years their junior. Over two decades of research, this unique cohort has shown phenotypic differences, including slower cortical thinning and robust social networks. This is the first study, however, to identify a specific genetic program and cellular “resilience signature” within the hippocampus that supports this plasticity.
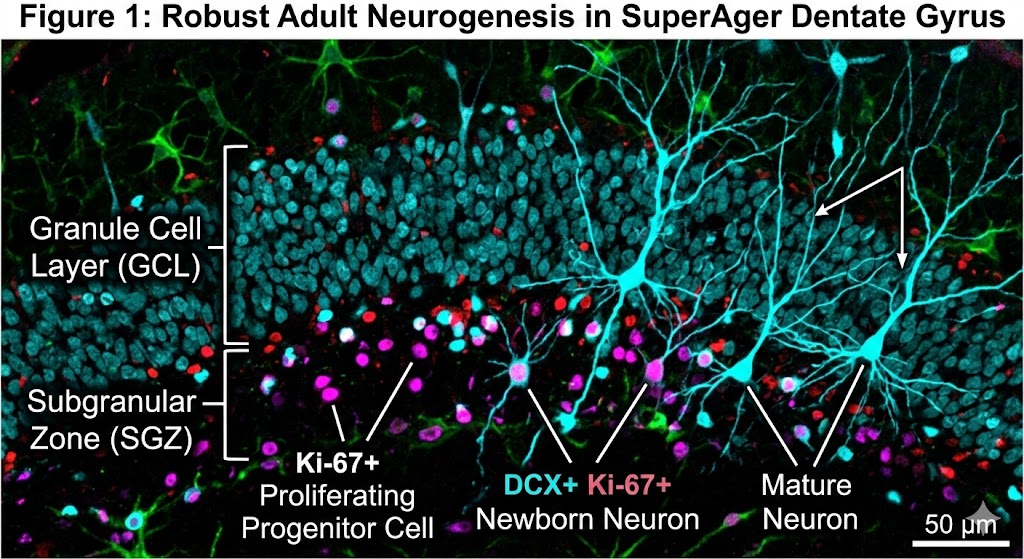
The scientific team, which included co-author Tamar Gefen, associate professor at Northwestern University, examined nearly 356,000 nuclei from the hippocampus regions of donated postmortem brains. They utilized multiomic single-cell sequencing—a specialized technique capable of simultaneously reading both gene activity and DNA accessibility (the “epigenetic landscape”) within single cells. This method allowed precise identification of cells at various developmental stages, from progenitor cells to immature and mature neurons.
The findings are compelling. SuperAgers were found to produce between two and two-and-a-half times more new neurons than their “typical” healthy peers and peers diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, respectively. Furthermore, the study identified a unique cellular environment in SuperAgers’ hippocampi that appears actively structured to support the birth and, crucially, the survival of these nascent cells.
The data shifts the conversation from merely “how do some brains resist decline?” to “how are some brains programmed to continuously renew?” The research suggests that the genetic programs supporting brain cell communication and survival remain active (“switched on”) in SuperAgers within key populations, specifically astrocytes and CA1 neurons. In contrast, these programs are “switched off” in cases of Alzheimer’s disease, particularly affecting excitatory synapses—the brain’s primary sites for memory formation.
This study provides tangible, biological proof that the aging brain can remain highly adaptable. It provides specific, concrete targets—such as preserving the integrity of excitatory synapses or modulating astrocytic profiles—for developing therapeutic interventions aimed at promoting healthy aging and preventing cognitive decline.
Questions for discussion: How do you anticipate these specific cell types (CA1 neurons and astrocytes) being targeted for therapeutic modulation? Given this study, where do you see the next five years of neurogenesis research focusing?
#Neuroscience #Neurogenesis #AgingResearch #Hippocampus #CognitiveResilience #Epigenetics
This high-resolution microscopy image corresponds to my scientific post. It features double-positive labeling for neurogenesis markers in a SuperAger brain, with distinct annotations differentiating newborn and mature neurons within the granule cell layer.